The World’s First EU AI Act Conformity Assessment Software Solution By AI Guardian
- Robin Hackney
- Feb 19, 2024
- 7 min read
Our simplified solution delivers cost-effective EU AI Act Conformity Assessment capabilities.
Fact Checked by Robin Hackney

With the European Union moving quickly to implement the Artificial Intelligence Act (AIA) companies the world-over are going to need to prepare for the first AI compliance requirements dictated by the AIA pertaining to their own organization’s AI efforts. Like all compliance, deliverables can be tricky and the penalties are steep for not getting it right. Today, AI Guardian is launching the first in-market software solution for delivering EU AI Act Conformity Assessment standards.
The Foundation: capAI Framework
Our AI Conformity Assessment solution follows the frameworks outlined in capAI which was created to apply ethics-based auditing best practices in the most effective format for conducting a Conformity Assessment in line with AIA stipulations. capAI is the product of the leading AI and ethics experts from The Centre for Digital Ethics at the University of Oxford and is considered the definitive framework for approaching AIA Conformity Assessments.
Comprehensive AI Conformity Assessment Components
AI Guardian partners can now easily produce a full range of AIA Conformity Assessment components including:

Internal Review Protocol (IRP): Provides organizations with a tool for AI quality assurance and risk management. By following the IRP, organizations can conduct conformity assessments in line with, and create the technical documentation required by, the AIA. It follows the development stages of the AI system’s lifecycle and assesses the organization’s awareness, performance, and resources in place to prevent, respond to and rectify potential failures. The IRP is designed to act as a document with restricted access, However, like accounting data, it may be disclosed in a legal context to support business-to-business contractual arrangements, or as evidence when responding to legal challenges related to the AI system audited.
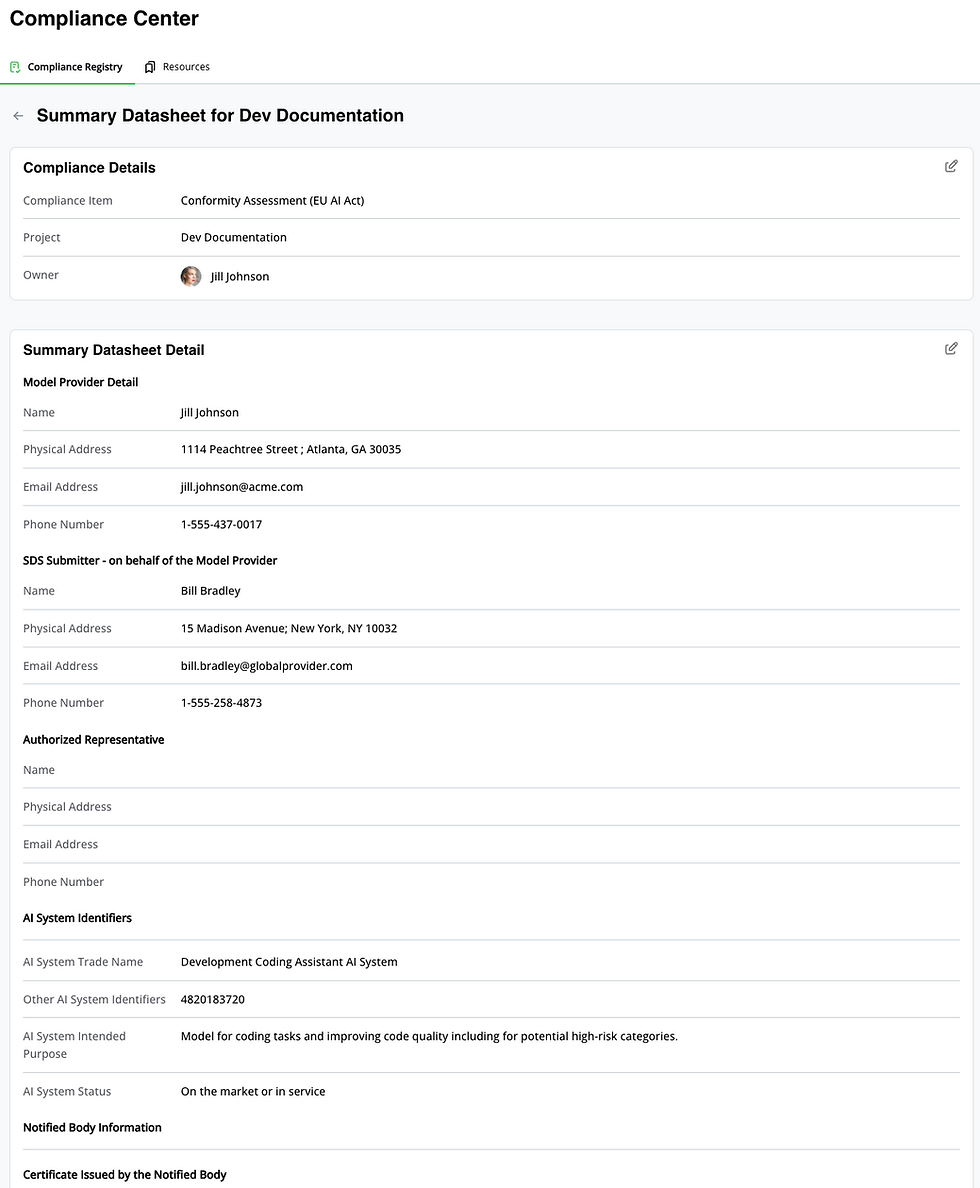
Summary Datasheets (SDS): To be submitted to the EU’s future public database on high-risk AI systems in operation. The SDS is a high-level summary of the AI system’s purpose, functionality and performance that fulfills the public registration requirements, as stated in the AIA.
External Scorecards (ESC): Can (optionally) be made available to customers and other stakeholders of the AI system. The ESC is generated through the IRP and summarizes relevant information about the AI system along four key dimensions: (1) purpose, (2) values, (3) data, and (4) governance. It is a public reference document that should be made available to all counterparties concerned.
Who Needs an AI Conformity Assessment?

Conformity Assessment components will be required for high-risk AI systems as outlined in Article 6(2) of the AIA and are highly recommended for minimal-risk AI systems. Indicative of high-risk AI systems are those used in recruitment, biometric identification surveillance systems, safety components (e.g., medical devices, automotive), access to essential private and public services (e.g., creditworthiness, benefits, health and life insurance), and safety of critical infrastructure (e.g., energy, transport). Even when not required for AIA compliance, companies are well advised to conduct Conformity Assessments across AI applications as a governance best practice and likely requirement for RFPs and other business relationships.
AI Guardian's Commitment to Regulatory Leadership
AI Guardian is focused on helping our partners be the leaders in their field on preparedness for continuing regulation and overall Responsible AI adherence. Our launch of Conformity Assessments within the AI Guardian platform is part of our continuing effort to lead on these subjects on behalf of our partners so they can adopt AI with confidence and accelerate their business results with the help of AI.
Contact us at info@aiguardianapp.com to learn more and on the full AI Guardian platform including our Conformity Assessment solution.
Deeper Dive: The Strategic Imperative of AI Compliance in the Evolving Technological Landscape
Why is AI Compliance Important?
In the swiftly changing technological landscape, AI compliance is not just a regulatory checkpoint but a strategic imperative. It serves as a key indicator of an organization's commitment to operating with integrity in the digital era. Achieving AI compliance is not simply about meeting legal requirements; it's about adopting a proactive stance in anticipation of future norms and regulations that will inevitably arise as AI technology continues to evolve and integrate across various sectors.
AI compliance is the pillar supporting ethical AI deployment. It mandates that all AI systems adhere to defined moral guidelines that prevent discrimination, uphold fairness, and guarantee the respect of human dignity. Consequently, when organizations embed these ethical tenets into their AI systems, they fortify consumer trust and enhance their corporate reputation.
Legal and Ethical Obligations in AI Utilization
Navigating AI's potential to reshape industries, organizations are bound by a dual mandate of legal compliance and ethical conduct. The gravity of responsibly deploying AI technologies cannot be overstated. AI is increasingly performing tasks that were previously the domain of human judgment, from sorting resumes for job applicants to determining eligibility for financial loans. Errors or biases in these systems could lead to significant harm to individuals and damage to an organization’s credibility.
Legal mandates serve as the necessary baseline, ensuring that AI systems do not infringe upon rights or create unjust outcomes. This requires thorough knowledge of both international regulations and local legislation that govern AI usage. More than ever, cross-functional teams within organizations, comprising legal experts, ethicists, and AI technologists, are needed to navigate this complex landscape.
Risk Mitigation through Rigorous Compliance Standards
Conforming to established standards attenuates risks significantly. Failure to comply with AI regulations can attract not only fines but also class-action lawsuits, lasting brand damage, and loss of consumer trust. It's mission-critical to stay ahead of regulatory trends to mitigate these risks.
Proper compliance is preventive medicine against the illnesses of legal challenges and public distrust. It demonstrates due diligence and dedication to ethical principles, reassuring stakeholders of an entity's integrity. In a way, it is an investment into the resilience and longevity of the company.
The Role of AI Compliance in Data Stewardship
At a practical level, AI compliance demands investment in the cornerstone of any AI system: data. Organizations must ensure the data used by AI systems is not only high-quality and relevant but also gathered and managed in adherence to strict privacy standards. This involves maintaining meticulous records, conducting regular audits, and applying principles of data minimization and anonymization wherever possible.
AI systems often utilize personal data to make predictions or decisions, which can have far-reaching implications for privacy. Effective compliance frameworks ensure these technologies are not intrusive and do not misuse personal information, safeguarding against breaches that may compromise sensitive data.
Understanding the Legislation: EU AI Act
The EU AI Act is a pioneering legislative framework that introduces a fresh, risk-centric approach to AI governance. It is an ambitious initiative that emphasizes not just compliance, but also sets a global benchmark for how AI can be used safely, transparently, and with respect for fundamental human rights.
The EU AI Act recognizes that AI is not inherently neutral; its design and deployment can pose risks that need to be managed with utmost discernment. The Act, therefore, categorizes AI systems according to the potential risk they pose to society and stipulates different degrees of regulatory scrutiny corresponding to those levels of risk.
Accountability and the AI Compliance Ecosystem
Who is Accountable for AI System Conformity Assessments?

Determining who bears the responsibility for AI Conformity Assessments (CAs) is crucial. The Act stipulates that these evaluations are generally the domain of AI system providers, who must ensure high levels of transparency and consumer protection. However, in cases where manufacturers or importers play a pivotal role in either the deployment or distribution of AI, responsibility may shift to correspond with their involvement.
This shared responsibility underlines the Act's intent; it is not only about individual accountability but also about fostering a comprehensive ecosystem where every stakeholder plays a part in upholding ethical AI standards.
Heightened Scrutiny in High-Risk AI Systems
AI technologies identified as carrying elevated risk necessitate stringent oversight. Such technologies include those deployed in critical infrastructures like transportation systems, where they have the potential to endanger public health and safety, as well as those used in the educational sector, such as exam scoring tools that could significantly influence one's access to education and career trajectory.
The distributor, importer, or any relevant third party is obliged to: ensure their quality management system adheres to the standards set out in Article 17, titled 'Quality Management System'; review the technical documentation to confirm that the high-risk AI system complies with necessary regulations; and check that both the development process of the AI system and the ongoing market surveillance, as detailed in Article 61, align with the aforementioned documentation.
Once this internal Conformity Assessment (CA) is carried out, the responsible body must compile and maintain a comprehensive EU declaration of conformity for each high-risk AI application.
Who Actually Makes Conformity Assessments?
The regulation makes a clear distinction between internal assessments, typically conducted for low or minimal-risk AI systems, and external assessments mandated for high-risk applications such as biometric identification. This bifurcation is essential, as it ensures that specialized, potentially more invasive technologies undergo stricter evaluation by impartial third parties to eliminate any biases and guarantee conformity to the highest standards.
The Seven Pillars of AI Conformity Assessments: Ensuring Comprehensive Compliance

The AI Act lays out a septet of assessment areas, forming a robust backbone for AI compliance. These include risk management measures, which necessitate a proactive approach to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential risks that AI systems might pose. Data governance strategies involve establishing clear protocols on the sourcing, storage, and usage of data within AI systems.
Technical documentation comes in as a detailed manual, providing transparency and clarity on how an AI system operates and the logic behind its decision-making processes.
Other areas cover record-keeping—maintaining exhaustive logs of AI system operations, transparency—providing lucid information to users, human oversight—ensuring there are checks to AI decision-making, and finally, a focus on accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity—certifying that the AI system is dependable and secure from both digital threats and operational failures.
Compliance with the AI Act is a dynamic, ongoing process, reflecting the fluid nature of AI's societal impact and the continuous advancements in technology. Non-compliance isn't merely penalized through financial means akin to GDPR fines; it has wider ramifications, potentially stalling AI innovation and adoption if trust in AI systems falters.
By adhering to these standards, organizations can confidently navigate the landscape of AI deployment, assuring that as the technology advances, it does so within the parameters of safety, fairness, and respect for every individual it may impact.
Advancing Compliance in the AI Landscape
In conclusion, balancing the power of artificial intelligence with necessitated regulatory compliance is pivotal for businesses forging into the digital era. The EU AI Act lays a potent framework for the ethical deployment of AI, presenting a chance for companies to proudly demonstrate their commitment to digital ethics and consumer protection.
Whether dealing with intricate AI systems within critical sectors or pioneering educational technologies, our conformity assessment solutions streamline the convergence of AI applications with regulatory standards. This commitment drives our process, providing you with a seamless passage to compliance and leadership in AI governance.
Schedule a demo with us and begin charting a robust and responsible course in the fast-expanding universe of AI technology.


Comments